Submit your email address to get a link for quick download on your desktop and get started!
Managing modern industrial facilities requires remote access to programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs). Companies can control, monitor, and diagnose issues from any location with remote access, minimizing downtime and increasing productivity.
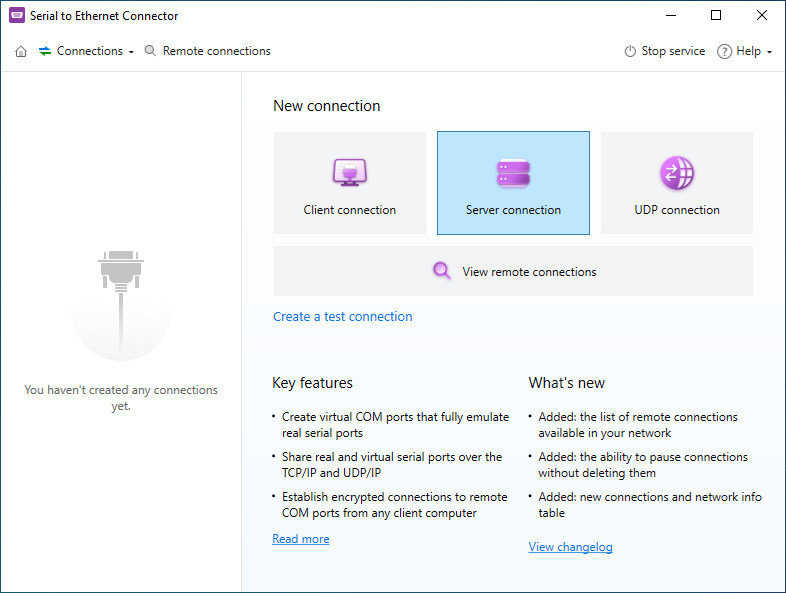
COM Port Redirector (ara Serial to Ethernet Connector) is a software utility that can be incorporated into industrial HMIs to provide remote access over Ethernet connections. The solution eliminates distance limitations and provides engineers with a powerful tool for monitoring and controlling systems and equipment.
Let’s take at the functionality and benefits available with Serial to Ethernet Connector.
PLCs are basic elements of industrial automation systems. A primary function of PLCs is to act as a stand-alone computer to control industrial equipment or processes. PLCs are often connected to a network as an integral part of a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system. The PLC is controlled through a combination of the infrastructure’s HMI and SCADA software.
An HMI is a software program that facilitates human interaction with PLCs. Human operators use an HMI to perform tasks such as monitoring, configuring, and controlling a PLC. An HMI can also provide alerts regarding system performance based on data generated by the PLC.
Some HMIs are simply a panel of lights and buttons that need to be operated manually when interacting with a PLC. More complex PLCs provide network connectivity and are typically attached to a computer running monitoring and programming capabilities. The majority of advanced PLCs have built-in communication ports and transfer data using the RS-232, RS-422, RS-485, or Ethernet protocols.
Configuring a PLC is done using its serial and USB port. The PLC is connected to a network hub via an Ethernet port. Operators access the PLC through the controlling servers and other network-connected equipment. Remote access to a PLC requires virtualized connections established through a software solution like Serial to Ethernet Connector.

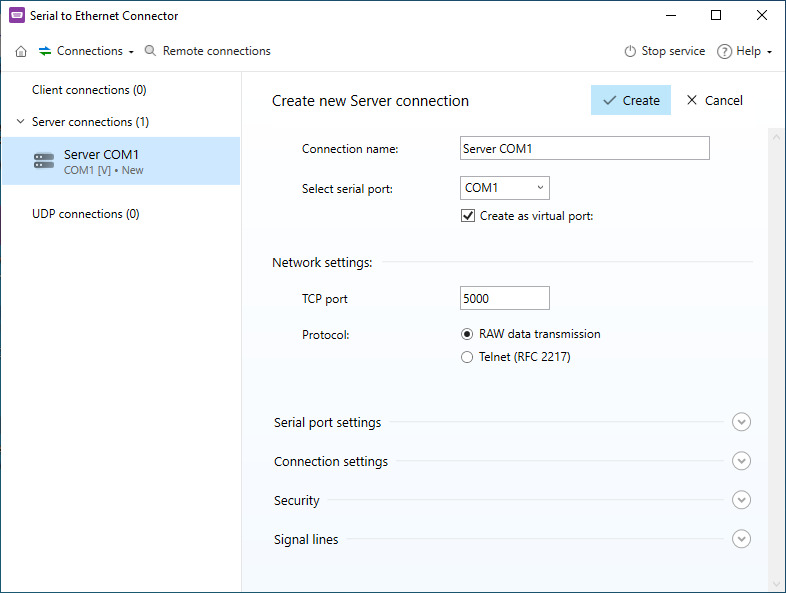
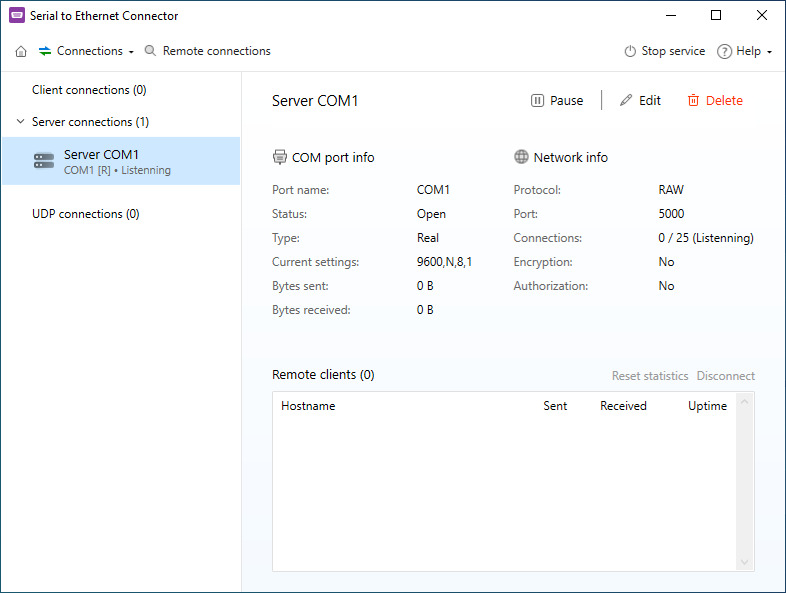
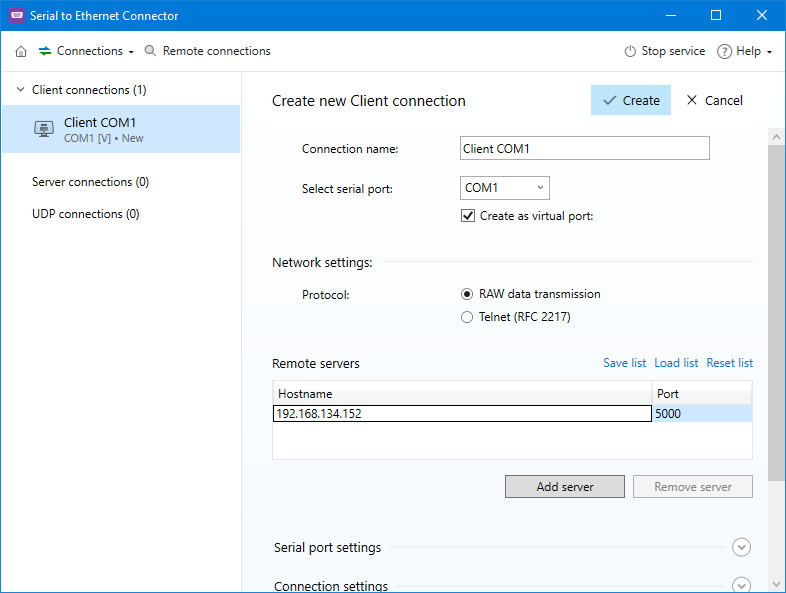
That’s all you need to establish remote access and control over a network-connected PLC with SEC.
Establishing remote PLC access with SEC provides industrial facilitates with the following benefits.

Related Articles
Serial to Ethernet Connector is our top choice for remote PLC access. Several alternate solutions are available that may pose some challenges for establishing remote connectivity to PLCs.
Remote desktop software - With remote desktop software, operators can indirectly access a PLC interface by controlling a computer physically located near the device. This solution can involve troubleshooting compatibility issues with operating systems, screen resolution problems, and bandwidth requirements.
Virtual private networks (VPNs) - A VPN establishes a secure Internet connection over which operators can remotely access a PLC. Additional configuration and monitoring may be necessary to use the VPN effectively. Its performance can be limited by network latency or insufficient bandwidth.
Cloud-based solutions - Remote access to PLC data is possible using scalable and flexible cloud platforms. Drawbacks to this approach include relying on the vendor’s infrastructure and possible data privacy concerns.
Dedicated remote access hardware - Remote access devices designed for use with PLCs are available from some manufacturers of industrial equipment. These devices usually provide sufficient security but may have limited features and flexibility when compared to a software solution such as a Serial to Ethernet Connector.
Multiple solutions are available for providing remote access to PLCs. Serial to Ethernet Connector is the best choice because of its strong security, advanced functionality, and seamless integration with existing infrastructure components. SEC promotes enhanced productivity by providing engineers with remote access to PLCs from HMIs. Remote access improves operational efficiency, reduces costs, and minimizes downtime for critical industrial systems. SEC offers a streamlined and effective method of providing the remote connectivity companies need to thrive in today’s competitive industrial landscape.
SEC for Windows
SEC for Linux